Adjacency Matrix Methods Example Java
Prerequisites: Graph and its representations
Given an adjacency matrix g[][] of a graph consisting of N vertices, the task is to modify the matrix after insertion of all edges[] and removal of edge between vertices (X, Y). In an adjacency matrix, if an edge exists between vertices i and j of the graph, then g[i][j] = 1 and g[j][i] = 1. If no edge exists between these two vertices, then g[i][j] = 0 and g[j][i] = 0.
Examples:
Input: N = 6, Edges[] = {{0, 1}, {0, 2}, {0, 3}, {0, 4}, {1, 3}, {2, 3}, {2, 4}, {2, 5}, {3, 5}}, X = 2, Y = 3
Output:
Adjacency matrix after edge insertion:
0 1 1 1 1 0
1 0 0 1 0 0
1 0 0 1 1 1
1 1 1 0 0 1
1 0 1 0 0 0
0 0 1 1 0 0
Adjacency matrix after edge removal:
0 1 1 1 1 0
1 0 0 1 0 0
1 0 0 0 1 1
1 1 0 0 0 1
1 0 1 0 0 0
0 0 1 1 0 0
Explanation:
The graph and the corresponding adjacency matrix after insertion of edges:
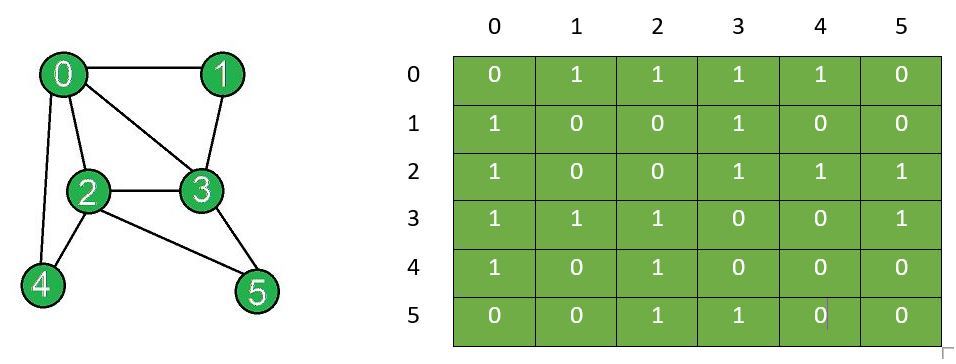
The graph after removal and adjacency matrix after removal of edge between vertex X and Y:
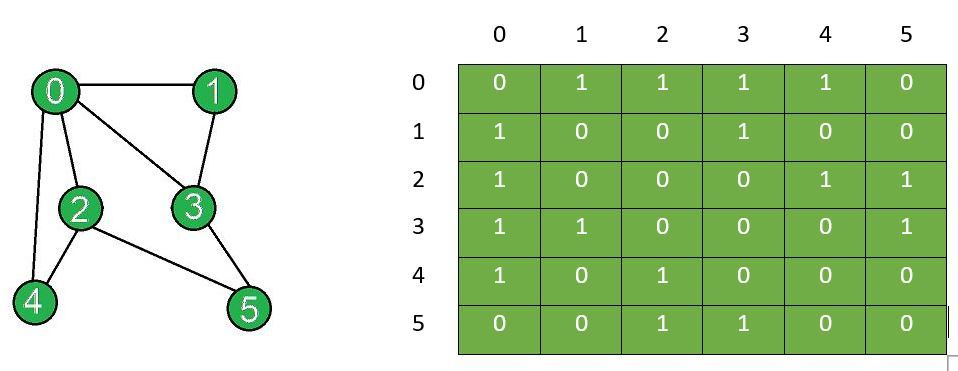
Input: N = 6, Edges[] = {{0, 1}, {0, 2}, {0, 3}, {0, 4}, {1, 3}, {2, 3}, {2, 4}, {2, 5}, {3, 5}}, X = 3, Y = 5
Output:
Adjacency matrix after edge insertion:
0 1 1 1 1 0
1 0 0 1 0 0
1 0 0 1 1 1
1 1 1 0 0 1
1 0 1 0 0 0
0 0 1 1 0 0
Adjacency matrix after edge removal:
0 1 1 1 1 0
1 0 0 1 0 0
1 0 0 1 1 1
1 1 1 0 0 0
1 0 1 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0 0
Approach:
Initialize a matrix of dimensions N x N and follow the steps below:
- Inserting an edge: To insert an edge between two vertices suppose i and j, set the corresponding values in the adjacency matrix equal to 1, i.e. g[i][j]=1 and g[j][i]=1 if both the vertices i and j exists.
- Removing an edge: To remove an edge between two vertices suppose i and j, set the corresponding values in the adjacency matrix equal to 0. That is, set g[i][j]=0 and g[j][i]=0 if both the vertices i and j exists.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Graph {
private :
int n;
int g[10][10];
public :
Graph( int x)
{
n = x;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for ( int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
g[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
void displayAdjacencyMatrix()
{
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cout << "\n" ;
for ( int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
cout << " " << g[i][j];
}
}
}
void addEdge( int x, int y)
{
if ((x < 0) || (x >= n)) {
cout << "Vertex" << x
<< " does not exist!" ;
}
if ((y < 0) || (y >= n)) {
cout << "Vertex" << y
<< " does not exist!" ;
}
if (x == y) {
cout << "Same Vertex!" ;
}
else {
g[y][x] = 1;
g[x][y] = 1;
}
}
void removeEdge( int x, int y)
{
if ((x < 0) || (x >= n)) {
cout << "Vertex" << x
<< " does not exist!" ;
}
if ((y < 0) || (y >= n)) {
cout << "Vertex" << y
<< " does not exist!" ;
}
if (x == y) {
cout << "Same Vertex!" ;
}
else {
g[y][x] = 0;
g[x][y] = 0;
}
}
};
int main()
{
int N = 6, X = 2, Y = 3;
Graph obj(N);
obj.addEdge(0, 1);
obj.addEdge(0, 2);
obj.addEdge(0, 3);
obj.addEdge(0, 4);
obj.addEdge(1, 3);
obj.addEdge(2, 3);
obj.addEdge(2, 4);
obj.addEdge(2, 5);
obj.addEdge(3, 5);
cout << "Adjacency matrix after"
<< " edge insertions:\n" ;
obj.displayAdjacencyMatrix();
obj.removeEdge(X, Y);
cout << "\nAdjacency matrix after"
<< " edge removal:\n" ;
obj.displayAdjacencyMatrix();
return 0;
}
Java
class Graph {
private int n;
private int [][] g = new int [ 10 ][ 10 ];
Graph( int x)
{
this .n = x;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) {
for ( int j = 0 ; j < n; ++j) {
g[i][j] = 0 ;
}
}
}
public void displayAdjacencyMatrix()
{
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) {
System.out.println();
for ( int j = 0 ; j < n; ++j) {
System.out.print( " " + g[i][j]);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
public void addEdge( int x, int y)
{
if ((x < 0 ) || (x >= n)) {
System.out.printf( "Vertex " + x
+ " does not exist!" );
}
if ((y < 0 ) || (y >= n)) {
System.out.printf( "Vertex " + y
+ " does not exist!" );
}
if (x == y) {
System.out.println( "Same Vertex!" );
}
else {
g[y][x] = 1 ;
g[x][y] = 1 ;
}
}
public void removeEdge( int x, int y)
{
if ((x < 0 ) || (x >= n)) {
System.out.printf( "Vertex " + x
+ " does not exist!" );
}
if ((y < 0 ) || (y >= n)) {
System.out.printf( "Vertex " + y
+ " does not exist!" );
}
if (x == y) {
System.out.println( "Same Vertex!" );
}
else {
g[y][x] = 0 ;
g[x][y] = 0 ;
}
}
}
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 6 , X = 2 , Y = 3 ;
Graph obj = new Graph(N);
obj.addEdge( 0 , 1 );
obj.addEdge( 0 , 2 );
obj.addEdge( 0 , 3 );
obj.addEdge( 0 , 4 );
obj.addEdge( 1 , 3 );
obj.addEdge( 2 , 3 );
obj.addEdge( 2 , 4 );
obj.addEdge( 2 , 5 );
obj.addEdge( 3 , 5 );
System.out.println( "Adjacency matrix after"
+ " edge insertions:" );
obj.displayAdjacencyMatrix();
obj.removeEdge( 2 , 3 );
System.out.println( "\nAdjacency matrix after"
+ " edge removal:" );
obj.displayAdjacencyMatrix();
}
}
Python3
class Graph:
__n = 0
__g = [[ 0 for x in range ( 10 )]
for y in range ( 10 )]
def __init__( self , x):
self .__n = x
for i in range ( 0 , self .__n):
for j in range ( 0 , self .__n):
self .__g[i][j] = 0
def displayAdjacencyMatrix( self ):
for i in range ( 0 , self .__n):
print ()
for j in range ( 0 , self .__n):
print (" ", self.__g[i][j], end = " ")
def addEdge( self , x, y):
if (x < 0 ) or (x > = self .__n):
print ( "Vertex {} does not exist!" . format (x))
if (y < 0 ) or (y > = self .__n):
print ( "Vertex {} does not exist!" . format (y))
if (x = = y):
print ( "Same Vertex!" )
else :
self .__g[y][x] = 1
self .__g[x][y] = 1
def removeEdge( self , x, y):
if (x < 0 ) or (x > = self .__n):
print ( "Vertex {} does not exist!" . format (x))
if (y < 0 ) or (y > = self .__n):
print ( "Vertex {} does not exist!" . format (y))
if (x = = y):
print ( "Same Vertex!" )
else :
self .__g[y][x] = 0
self .__g[x][y] = 0
obj = Graph( 6 );
obj.addEdge( 0 , 1 )
obj.addEdge( 0 , 2 )
obj.addEdge( 0 , 3 )
obj.addEdge( 0 , 4 )
obj.addEdge( 1 , 3 )
obj.addEdge( 2 , 3 )
obj.addEdge( 2 , 4 )
obj.addEdge( 2 , 5 )
obj.addEdge( 3 , 5 )
print ( "Adjacency matrix after "
"edge insertions:\n" )
obj.displayAdjacencyMatrix();
obj.removeEdge( 2 , 3 );
print ( "\nAdjacency matrix after "
"edge removal:\n" )
obj.displayAdjacencyMatrix();
C#
using System;
class Graph{
private int n;
private int [,] g = new int [10, 10];
public Graph( int x)
{
this .n = x;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
for ( int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
{
g[i, j] = 0;
}
}
}
public void displayAdjacencyMatrix()
{
for ( int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
Console.WriteLine();
for ( int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
{
Console.Write( " " + g[i, j]);
}
}
}
public void addEdge( int x, int y)
{
if ((x < 0) || (x >= n))
{
Console.WriteLine( "Vertex {0} does " +
"not exist!" , x);
}
if ((y < 0) || (y >= n))
{
Console.WriteLine( "Vertex {0} does " +
"not exist!" , y);
}
if (x == y)
{
Console.WriteLine( "Same Vertex!" );
}
else
{
g[y, x] = 1;
g[x, y] = 1;
}
}
public void removeEdge( int x, int y)
{
if ((x < 0) || (x >= n))
{
Console.WriteLine( "Vertex {0} does" +
"not exist!" , x);
}
if ((y < 0) || (y >= n))
{
Console.WriteLine( "Vertex {0} does" +
"not exist!" , y);
}
if (x == y)
{
Console.WriteLine( "Same Vertex!" );
}
else
{
g[y, x] = 0;
g[x, y] = 0;
}
}
}
class GFG{
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Graph obj = new Graph(6);
obj.addEdge(0, 1);
obj.addEdge(0, 2);
obj.addEdge(0, 3);
obj.addEdge(0, 4);
obj.addEdge(1, 3);
obj.addEdge(2, 3);
obj.addEdge(2, 4);
obj.addEdge(2, 5);
obj.addEdge(3, 5);
Console.WriteLine( "Adjacency matrix after " +
"edge insertions:\n" );
obj.displayAdjacencyMatrix();
obj.removeEdge(2, 3);
Console.WriteLine( "\nAdjacency matrix after " +
"edge removal:" );
obj.displayAdjacencyMatrix();
}
}
Javascript
<script>
var n = 0;
var g = Array.from(Array(10), ()=>Array(10).fill(0));
function initialize(x)
{
n = x;
for ( var i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
for ( var j = 0; j < n; ++j)
{
g[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
function displayAdjacencyMatrix()
{
for ( var i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
document.write( "<br>" );
for ( var j = 0; j < n; ++j)
{
document.write( " " + g[i][j]);
}
}
}
function addEdge(x, y)
{
if ((x < 0) || (x >= n))
{
document.write(`Vertex ${x} does not exist!`);
}
if ((y < 0) || (y >= n))
{
document.write(`Vertex ${y} does not exist!`);
}
if (x == y)
{
document.write( "Same Vertex!<br>" );
}
else
{
g[y][x] = 1;
g[x][y] = 1;
}
}
function removeEdge(x, y)
{
if ((x < 0) || (x >= n))
{
document.write(`Vertex ${x} does not exist!`);
}
if ((y < 0) || (y >= n))
{
document.write(`Vertex ${y} does not exist!`);
}
if (x == y)
{
document.write( "Same Vertex!<br>" );
}
else
{
g[y][x] = 0;
g[x][y] = 0;
}
}
initialize(6);
addEdge(0, 1);
addEdge(0, 2);
addEdge(0, 3);
addEdge(0, 4);
addEdge(1, 3);
addEdge(2, 3);
addEdge(2, 4);
addEdge(2, 5);
addEdge(3, 5);
document.write( "Adjacency matrix after " +
"edge insertions:<br>" );
displayAdjacencyMatrix();
removeEdge(2, 3);
document.write( "<br>Adjacency matrix after " +
"edge removal:<br>" );
displayAdjacencyMatrix();
</script>
Output:
Adjacency matrix after edge insertions: 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 Adjacency matrix after edge removal: 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0
Time Complexity: Insertion and Deletion of an edge requires O(1) complexity while it takes O(N2) to display the adjacency matrix.
Auxiliary Space: O(N2)
Source: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/add-and-remove-edge-in-adjacency-matrix-representation-of-a-graph/
0 Response to "Adjacency Matrix Methods Example Java"
Post a Comment